
Face recognition technology has existed for quite some time, but until recently face analysis was not accurate enough for most purposes.
Now it seems that face recognition is everywhere:
The reason why facial recognition software has recently got a lot better and a lot faster is due to the advent of deep learning: more powerful and parallelised computers, and better software design.
I’m going to talk about what’s changed.
The first serious attempts to build a face recogniser were back in the 1980s and 90s and used something called Eigenfaces. An Eigenface is a blurry face-like image, and a face recogniser assumes that every face is made of lots of these images overlaid on top of each other pixel by pixel.

If we want to recognise an unknown face we just work out which Eigenfaces it’s likely to be composed of.
Not surprisingly the Eigenface method didn’t work very well. If you shift a face image a few pixels to the right or left, you can easily see how this method will fail, since the parts of the face won’t line up with the eigenface any more.
Fast Data Science - London
The next generation of face recognisers would take each face image and find important points such as the corner of the mouth, or an eyebrow. The coordinates of these points are called facial feature points. One well known commercial program converts every face into 66 feature points.
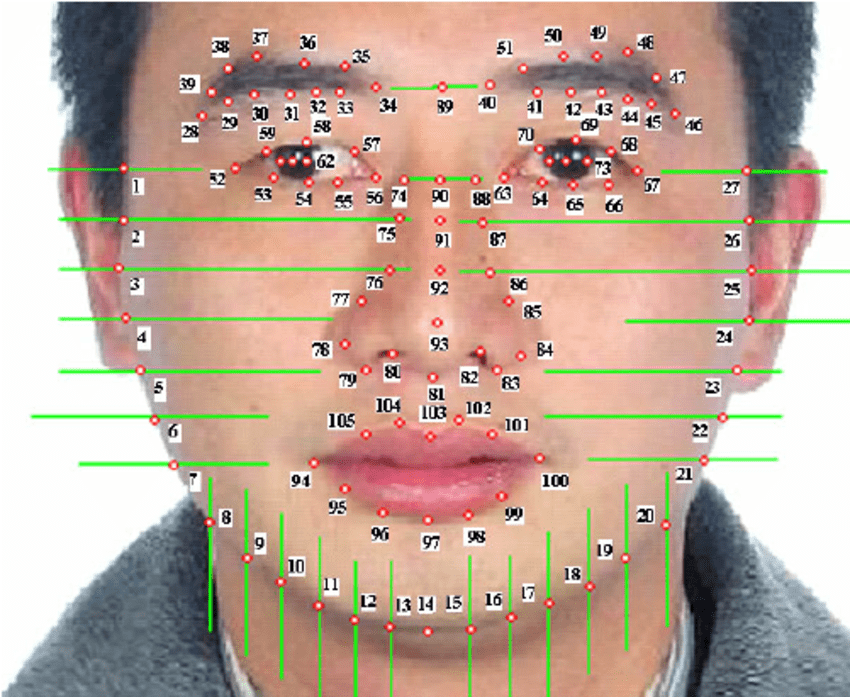
Facial feature points, an hand coded method of face recognition technology. Image source
To compare two faces you simply compare the coordinates (after adjusting in case one image is slightly off alignment).
Not surprisingly the facial feature coordinates method is better than the Eigenfaces method but is still suboptimal. We are throwing lots of useful information away: hair colour, eye colour, any facial structure that isn’t captured by a feature point, etc.
The last face analysis method in particular involved a human programming into a computer the definition of an “eyebrow” etc. The current generation of machine learning face recognition models throws all this out of the window.
This approach used convolutional neural networks (CNNs). This involves repeatedly walking a kind of stencil over the image and working out where subsections of the image match particular patterns.
The first time, you pick up corners and edges. After doing this five times, each time on the output of the previous run, you start to pick up parts of an eye or ear. After 30 times, you have recognised a whole face!
The neat trick is that nobody has defined the patterns that we are looking for but rather they come from training the network with millions of face images.
Of course this can be an Achilles’ heel of the CNN approach since you may have no idea exactly why a face recogniser gave a particular answer.
The obstacle you encounter if you want to develop your own CNN face recogniser is, where can you get millions of images to develop the model? Lots of people scrape celebrity images from the internet to do this.
However you can get much more images if you can get people to give you their personal photos for free!
This is the reason why Facebook, Microsoft and Google have some of the most accurate face recognisers, since they have access to the resources necessary to train the machine learning models for facial recognition.
The CNN approach is far from perfect and many companies will have some adjustments on top of what I described in order to compensate for its limitations, such as correcting for pose and lighting, often using a 3D mesh model of the face.
Machine learning facial recognition models are advancing rapidly and every year the state of the art in face recognition and analysis brings a noticeable improvement.
If you’d like to know more about this field, similar projects, or want to implement business applications of machine learning facial recognition models in 2024 - please get in touch.
Unleash the potential of your NLP projects with the right talent. Post your job with us and attract candidates who are as passionate about natural language processing.
Hire NLP Experts
We are excited to introduce the new Harmony Meta platform, which we have developed over the past year. Harmony Meta connects many of the existing study catalogues and registers.

Guest post by Jay Dugad Artificial intelligence has become one of the most talked-about forces shaping modern healthcare. Machines detecting disease, systems predicting patient deterioration, and algorithms recommending personalised treatments all once sounded like science fiction but now sit inside hospitals, research labs, and GP practices across the world.
If you are developing an application that needs to interpret free-text medical notes, you might be interested in getting the best possible performance by using OpenAI, Gemini, Claude, or another large language model. But to do that, you would need to send sensitive data, such as personal healthcare data, into the third party LLM. Is this allowed?
What we can do for you