
Artificial intelligence (AI) is not just a buzzword; it’s a transformative force reshaping various industries, with finance and investment standing at the forefront of this revolution. The application of AI in investment strategies is ushering in a new era of precision, speed, and predictive power, enabling investors to make more informed decisions with unprecedented efficiency. From robo-advisors that provide personalized investment advice to sophisticated algorithms that predict market trends, AI is becoming an indispensable tool for both individual investors and large financial institutions. However, the rapid advancements in AI technology bring both opportunities and challenges. Investors must navigate a landscape that is continually evolving, with AI systems that can be as complex as they are powerful. Understanding how to leverage these technologies effectively is crucial for staying ahead in the competitive world of finance. This blog will delve into the current state of AI in the investment sector, exploring the myriad benefits it offers, the inherent risks involved, and providing practical advice for those looking to harness the power of AI in their investment strategies.
AI’s entry into the financial world is not a recent phenomenon. Over the past decade, financial institutions have increasingly turned to AI to optimize trading strategies, manage risk, and enhance customer experiences.
Machine Learning in Trading: machine learning algorithms are at the heart of many AI-driven trading strategies. These algorithms can sift through vast amounts of historical and real-time market data, identifying patterns and correlations that may be too complex or subtle for human traders to detect. By leveraging these insights, machine learning models can predict future price movements with remarkable accuracy, allowing hedge funds and investment banks to execute trades at speeds and with a precision that far surpasses human capabilities.
Robo-Advisors: The advent of robo-advisors has been one of the most significant innovations in personal finance, democratizing investment management by making it accessible to a wider audience. These automated platforms utilize AI-driven algorithms to assess an investor’s risk tolerance, financial goals, and market conditions, constructing and managing a diversified portfolio tailored to the individual’s needs. With lower fees compared to traditional financial advisors and the ability to provide personalized investment strategies at scale, robo-advisors have attracted millions of users, particularly those who prefer a hands-off approach to investing.
Sentiment Analysis: Beyond analyzing numerical data, AI is increasingly being used to gauge the mood of the market through sentiment analysis. By processing vast amounts of unstructured data from news articles, social media, blogs, and other online sources, AI systems can detect shifts in public sentiment toward specific stocks, sectors, or the market as a whole. For example, a surge in negative sentiment surrounding a particular company could indicate potential risks, prompting investors to adjust their strategies accordingly.
To better understand how AI is used in the financial industry, let’s look at some specific use cases across different areas of investment.
| Use Case | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| High-Frequency Trading | AI algorithms execute trades in milliseconds, taking advantage of minor price discrepancies. | Maximizes profits by exploiting short-term market movements. |
| Algorithmic Trading | AI-driven algorithms predict price movements based on historical data and execute trades. | Increases trading efficiency and reduces human error. |
| Portfolio Optimization | AI assesses risk and return profiles to build and rebalance diversified portfolios automatically. | Enhances portfolio performance while maintaining desired risk levels. |
| Use Case | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Robo-Advisors | AI-driven platforms provide automated financial advice and portfolio management services. | Makes financial planning accessible to a broader audience at a lower cost. |
| Chatbots and Virtual Assistants | AI-powered chatbots assist customers with account management and investment queries. | Enhances customer experience by providing instant and accurate support. |
| Personalized Marketing | AI analyzes customer data to tailor investment products and services to individual preferences. | Increases customer engagement and satisfaction. |
AI offers several advantages over traditional investment approaches, transforming how decisions are made and portfolios are managed:
Speed and Efficiency: AI algorithms excel in processing and analyzing vast amounts of data at speeds far beyond human capabilities. In the fast-paced world of finance, where market conditions can change in an instant, this ability to make real-time decisions is crucial. AI can quickly identify emerging trends, execute trades, and adjust strategies in response to market fluctuations, providing a significant edge in volatile environments.
Data-Driven Decisions: The sheer volume of data available in today’s markets is overwhelming for human analysts. AI can comb through this data, from historical price trends to macroeconomic indicators, and uncover patterns and insights that might otherwise go unnoticed. This deep analysis. enables more informed investment decisions, potentially leading to higher returns.
Reduced Emotional Bias: Human emotions, such as fear and greed, can lead to irrational investment decisions, such as panic selling during market downturns or holding onto losing positions for too long. AI systems, however, operate based purely on data and predefined algorithms, eliminating the influence of emotional bias.
Customization and Personalization: Traditionally, personalized investment advice was a luxury reserved for high-net-worth individuals who could afford personal financial advisors. AI has democratized this aspect of investing by making customization accessible to a broader audience. AI-powered platforms can analyze an individual’s financial goals, risk tolerance, investment horizon, and even preferences, to create and manage a portfolio tailored specifically to their needs.
Cost Efficiency: Another significant benefit of AI-driven investment strategies is the reduction in costs. By automating many of the tasks that would traditionally require manual intervention, such as portfolio rebalancing and risk assessment, AI platforms can operate with lower overheads. This efficiency is often passed on to investors in the form of lower fees, making professional-grade investment management more accessible to a wider range of people.
24/7 Market Monitoring: AI systems can operate around the clock, monitoring global markets and reacting to changes even outside of traditional trading hours. This ensures that opportunities are not missed and that portfolios are constantly adjusted to reflect the latest market conditions. For investors, this means greater peace of mind knowing that their investments are being managed continuously, without the limitations of human working hours.
Scalability: AI-driven platforms can manage vast numbers of portfolios simultaneously, each with its unique strategy, without the need for additional resources. This scalability is particularly beneficial for financial institutions managing a large number of clients, as it allows for consistent and high-quality service across the board.
While AI offers significant advantages, it also presents unique risks and challenges:
Algorithmic Bias: AI systems are only as good as the data they are trained on. If the training data is biased, the AI’s predictions and decisions will also be biased, potentially leading to suboptimal investment outcomes.
Overfitting: AI models might become too closely aligned with historical data, leading to overfitting. This means the model performs exceptionally well on historical data but fails to generalize to new, unseen data, resulting in poor investment decisions.
Transparency and Accountability: AI algorithms can be opaque, making it difficult for investors to understand how decisions are being made. This lack of transparency can lead to mistrust and ethical concerns, particularly when an AI-driven strategy underperforms.
Regulatory Concerns: As AI becomes more prevalent in finance, regulators are grappling with how to ensure these systems are used responsibly. There is a risk that regulatory bodies may struggle to keep pace with technological advancements, leading to gaps in oversight.
| Risk Factor | Description | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Algorithmic Bias | Bias in training data leading to skewed predictions. | Regular audits and diversification of data sources. |
| Overfitting | Model is too tailored to past data, failing on new data. | Use of cross-validation and diverse datasets. |
| Transparency Issues | Difficulty in understanding AI decisions due to the complexity of algorithms. | Implement explainable AI (XAI) techniques. |
| Regulatory Uncertainty | Potential for gaps in regulation due to rapid AI advancements. | Stay updated on regulatory changes and participate in AI governance. |
While AI offers significant advantages in investment strategies, it also presents unique risks and challenges that must be carefully managed to ensure successful outcomes:
Algorithmic Bias: AI systems are inherently reliant on the data they are trained on. If this data contains biases—whether due to historical inequalities, market anomalies, or incomplete information—these biases can be perpetuated in the AI’s predictions and decisions. This could result in suboptimal investment outcomes, particularly if the AI model overemphasizes certain trends or ignores others due to biased data.
Overfitting: One of the common pitfalls in AI modeling is overfitting, where a model becomes too closely aligned with historical data. While this can lead to impressive performance on past data, it often results in poor generalization to new, unseen data. In the context of investments, overfitting can cause an AI model to make erroneous predictions or to fail when market conditions change.
Transparency and Accountability: AI algorithms, particularly those involving deep learning and complex neural networks, are often referred to as “black boxes” due to their opaque nature. Investors may find it challenging to understand how and why certain decisions are being made, leading to a lack of trust in the system. This lack of transparency can also create significant ethical concerns, especially when AI-driven strategies underperform or when they make decisions that are difficult to justify or explain.
Regulatory Concerns: The rapid pace of AI adoption in finance is outstripping the ability of regulatory bodies to keep up. This creates potential risks as regulations may lag behind the technology, leaving gaps in oversight that could be exploited or result in unintended consequences. The uncertainty around how AI will be regulated in the future adds an additional layer of risk for investors and financial institutions.
Model Drift: AI models can experience “drift” over time, where their predictive accuracy deteriorates as market conditions evolve and deviate from the conditions present during the training phase. This can lead to increasingly inaccurate predictions and poor investment decisions if the models are not regularly updated and recalibrated. Monitoring and maintaining the relevance of AI models is an ongoing challenge, particularly in fast-changing markets.
Cybersecurity Risks: As AI systems become more integrated into financial platforms, they also become potential targets for cyberattacks. Hackers could manipulate AI algorithms, corrupt data, or exploit vulnerabilities in automated trading systems to cause financial harm. Ensuring the security of AI-driven investment platforms is essential to prevent these risks, but it requires constant vigilance and robust cybersecurity measures.
| Risk Factor | Description | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Algorithmic Bias | Bias in training data leading to skewed predictions. | Regular audits and diversification of data sources. |
| Overfitting | Model is too tailored to past data, failing on new data. | Use of cross-validation and diverse datasets. |
| Transparency Issues | Difficulty in understanding AI decisions due to the complexity of algorithms. | Implement explainable AI (XAI) techniques. |
| Regulatory Uncertainty | Potential for gaps in regulation due to rapid AI advancements. | Stay updated on regulatory changes and participate in AI governance. |
| Model Drift | Degradation of model accuracy over time due to changing market conditions. | Regular updates and retraining of AI models. |
| Cybersecurity Risks | Vulnerabilities in AI systems that could be exploited by cyberattacks. | Implement strong cybersecurity measures and regular audits. |
Given the benefits and risks associated with AI in investment, here are some practical tips for investors looking to integrate AI into their strategies:
Educate Yourself: Before diving into AI-driven investments, it’s crucial to understand how these technologies work. Familiarize yourself with the basics of AI, machine learning, and their applications in finance. Consider taking courses, attending webinars, or reading up on AI trends in the financial sector. The better your understanding, the more confidently you can incorporate AI into your investment strategy.
Start Small: If you’re new to AI investments, consider starting with a small portion of your portfolio. This approach allows you to gain experience and learn how AI-driven tools and platforms operate without risking a significant portion of your assets. As you become more comfortable and confident, you can gradually increase your exposure to AI-driven investments.
Diversify: AI can enhance diversification by identifying uncorrelated assets and optimizing portfolio allocation. However, it’s important to ensure that your portfolio remains diversified across different asset classes, sectors, and regions. Diversification is a fundamental risk management strategy that can help cushion your portfolio against market volatility and sector-specific downturns.
Monitor Performance: Regularly review the performance of your AI-driven investments. While AI systems can be highly effective, they are not infallible. Keep an eye on how your investments are performing relative to your goals and the broader market. Consider setting up automated alerts to notify you of significant changes or performance thresholds. This proactive approach helps you make timely adjustments to your portfolio as needed.
Stay Informed: The AI and finance sectors are constantly evolving. Stay up-to-date with the latest developments, including new AI technologies, regulatory changes, and market trends. This knowledge will enable you to make informed decisions and adapt your investment strategy to leverage new opportunities or mitigate emerging risks. Subscribing to financial newsletters, joining investment forums, and following thought leaders in AI and finance are good ways to stay informed.
Understand the Costs: AI-driven investment platforms often come with different fee structures than traditional investment vehicles. Be sureqqqqq to understand the costs associated with using these platforms, including management fees, transaction costs, and any other expenses that might impact your overall returns. Compare the costs with the potential benefits to ensure that the AI-driven approach is cost-effective for your investment goals.
| Tip | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Start Small | Begin with a small portion of your portfolio to minimize risk. | Invest 5-10% of your total portfolio in AI-driven funds. |
| Diversify | Use AI to diversify across sectors and asset classes. | Combine AI-driven ETFs with traditional index funds. |
| Regular Monitoring | Continuously monitor the performance of your AI-driven investments. | Set up automated alerts for performance thresholds. |
| Stay Informed | Keep up with the latest developments in AI and finance. | Subscribe to financial AI newsletters and reports. |
| Understand the Costs | Be aware of the fee structures associated with AI-driven platforms. | Compare management fees and transaction costs before investing. |
The role of AI in investment is set to expand further in the coming years, driven by ongoing technological advancements and the evolving needs of investors. Here are some key trends and developments to watch for:
AI-Powered ETFs: Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) driven by AI are expected to grow in popularity. These funds use sophisticated AI algorithms to select and manage a portfolio of assets, continuously optimizing the selection based on real-time data and market trends. AI-powered ETFs offer investors a new way to gain exposure to AI-driven strategies without the need for hands-on management.
Integration with Blockchain: The combination of AI and blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize the financial industry. AI can be used to analyze the vast amounts of data stored on blockchain networks, uncovering insights that can be used to predict cryptocurrency price movements, optimize trading strategies, and enhance transparency in financial transactions.
Increased Regulation: As AI’s influence in finance continues to grow, so too will regulatory scrutiny. Governments and regulatory bodies are expected to implement more robust frameworks to ensure that AI-driven systems are transparent, fair, and accountable. Future regulations may require financial institutions to provide greater transparency into how AI models are trained, the data they use, and the decision-making processes they follow.
Ethical AI: As AI becomes more deeply embedded in the financial industry, there will likely be a growing emphasis on ethical AI practices. Concerns about the societal impact of AI, including issues related to fairness, bias, and the potential for job displacement, will drive demand for AI systems that prioritize social responsibility and sustainability alongside profitability.
Personalized AI Investment Advisors: The future may see the rise of highly personalized AI investment advisors, capable of tailoring financial advice to an individual’s unique financial situation, goals, and risk tolerance. These AI advisors would use advanced data analytics and machine learning to continuously refine their recommendations based on changes in the market and the investor’s circumstances.
AI-Driven Financial Literacy Tools: As AI becomes more integral to investing, there may also be an increase in AI-driven tools aimed at improving financial literacy. These tools could use AI to offer personalized educational content, helping investors of all levels understand complex financial concepts and make more informed decisions.
As AI becomes more deeply embedded in the financial world, ethical considerations are becoming increasingly critical. Key ethical issues such as algorithmic transparency, data privacy, and the potential for job displacement in the financial sector are at the forefront of these concerns.
Algorithmic Transparency: One of the most pressing ethical concerns with AI in finance is the opacity of many AI systems. These “black box” algorithms can make decisions that are difficult for humans to interpret or understand, leading to a lack of transparency. Investors should demand greater transparency from AI systems, ensuring they understand how decisions are made, what data is being used, and the underlying assumptions driving those decisions.
Data Privacy: AI systems in finance rely on vast amounts of personal and financial data to make accurate predictions and provide personalized investment advice. However, the collection, processing, and storage of this data raise significant privacy concerns. Investors should be aware of how their data is being used and stored by AI platforms, and they should demand robust data protection measures to safeguard their information.
Job Displacement: The rise of AI in finance has the potential to disrupt traditional employment patterns, particularly in roles that have historically been performed by human analysts, traders, and financial advisors. As AI systems take over more routine tasks, there is a risk of significant job losses in the financial sector. This presents a challenge not only for those whose jobs may be at risk but also for society as a whole.
Fairness and Bias: AI systems are only as unbiased as the data they are trained on. If training data contains biases, these can be perpetuated and even amplified by AI algorithms, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes. This is particularly concerning in finance, where biased decisions could affect lending practices, investment opportunities, and access to financial services.
AI is undeniably transforming the investment landscape, offering unprecedented opportunities for those who are willing to embrace its potential. From enhancing trading strategies and personalizing investment advice to automating routine tasks, AI is paving the way for more efficient, data-driven, and precise financial decision-making. For investors, the adoption of AI presents the chance to achieve better outcomes, reduce human errors, and access sophisticated tools that were once reserved for only the largest institutions. However, with these opportunities come significant challenges and risks that must be carefully managed. The complexities of AI, including issues related to algorithmic bias, transparency, data privacy, and potential job displacement, highlight the importance of a thoughtful and responsible approach to its integration in finance. As AI continues to evolve and permeate the financial industry, collaboration between investors, financial institutions, and regulators will be crucial. This collaboration is needed to establish ethical standards, ensure fairness, and maintain trust in AI-driven systems. By working together, stakeholders can address the ethical considerations and regulatory challenges that accompany AI, thereby ensuring that it is used responsibly and for the benefit of all. In the end, the true potential of AI in finance lies in its ability to create a more efficient, equitable, and prosperous financial system. By harnessing AI’s capabilities while adhering to ethical principles, we can move towards a future where technology not only enhances financial performance but also contributes to the broader good. The AI revolution in finance is just beginning, and those who approach it with both enthusiasm and caution will be best positioned to thrive in this new era.
Looking for experts in Natural Language Processing? Post your job openings with us and find your ideal candidate today!
Post a Job
Fast Data Science appeared at the Hamlyn Symposium event on “Healing Through Collaboration: Open-Source Software in Surgical, Biomedical and AI Technologies” Thomas Wood of Fast Data Science appeared in a panel at the Hamlyn Symposium workshop titled “Healing Through Collaboration: Open-Source Software in Surgical, Biomedical and AI Technologies”. This was at the Hamlyn Symposium on Medical Robotics on 27th June 2025 at the Royal Geographical Society in London.
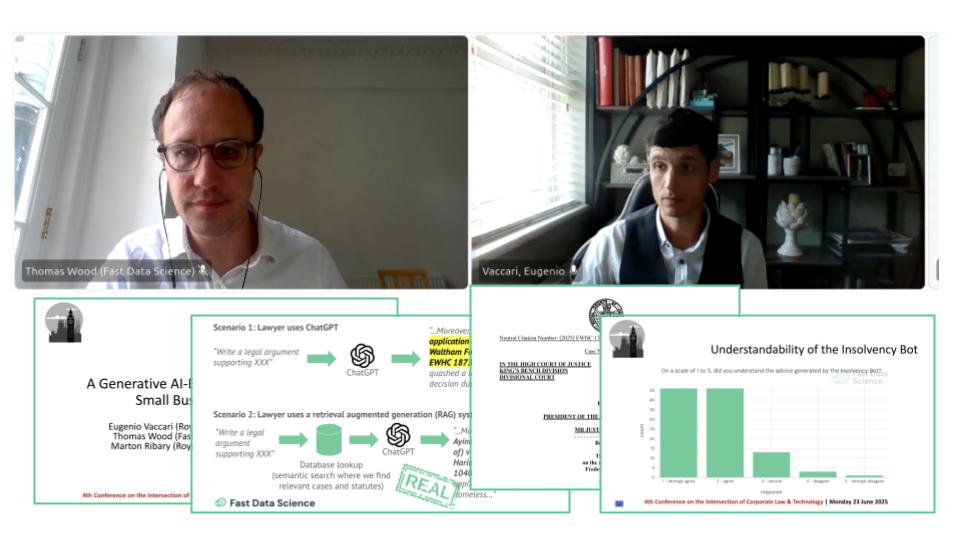
We presented the Insolvency Bot at the 4th Annual Conference on the Intersection of Corporate Law and Technology at Nottingham Trent University Dr Eugenio Vaccari of Royal Holloway University and Thomas Wood of Fast Data Science presented “A Generative AI-Based Legal Advice Tool for Small Businesses in Distress” at the 4th Annual Conference on the Intersection of Corporate Law and Technology at Nottingham Trent University

What is generative AI consulting? We have been taking on data science engagements for a number of years. Our main focus has always been textual data, so we have an arsenal of traditional natural language processing techniques to tackle any problem a client could throw at us.
What we can do for you