
The Clinical Trial Risk Tool has been featured in a guest column by Thomas Wood, director of Fast Data Science, in Clinical Leader, titled A Tool To Tackle The Risk Of Uninformative Trials, in cooperation with Abby Proch, Executive Editor at Clinical Leader.
In this article, Thomas Wood discusses the issue of uninformative clinical trials in pharmaceutical research. Uninformative trials fail to provide meaningful results, either because they don’t address key questions or are poorly designed. These trials waste resources, expose participants to unnecessary risks, and hinder progress in medical knowledge.
Wood uses the definition of “uninformative trials” from Zarin et al (2019)[1] as trials that do not deliver informative results, even though the investigated treatment may be effective or ineffective. An informative trial, according to experts, must meet five conditions: addressing an important question, providing meaningful evidence, being feasible, conducted scientifically, and reporting methods and results promptly.
The Clinical Trial Risk Tool was created to prevent such trials by providing features like a clinical trial budget estimator based on real-world cost data. The development of the first version of the tool was published in Gates Open Research[2]. In future, the tool could retrieve past trials with similar endpoints or inclusion/exclusion criteria to improve protocol design. It could also generate personalised feedback for different stakeholders, such as medical professionals, financial planners, and patient advocates.
Fast Data Science’s Clinical Trial Risk Tool offers a solution by allowing users to upload trial protocols, where AI analyzes the document for risk and cost factors. The tool estimates trial costs and identifies risks, helping to avoid uninformative outcomes early in the design process.
Unleash the potential of your NLP projects with the right talent. Post your job with us and attract candidates who are as passionate about natural language processing.
Hire NLP Experts
None of the content of this article constitutes investment advice. Few would dispute that the global economy is currently in an AI boom. However, opinions are divided over whether this boom also constitutes a bubble.
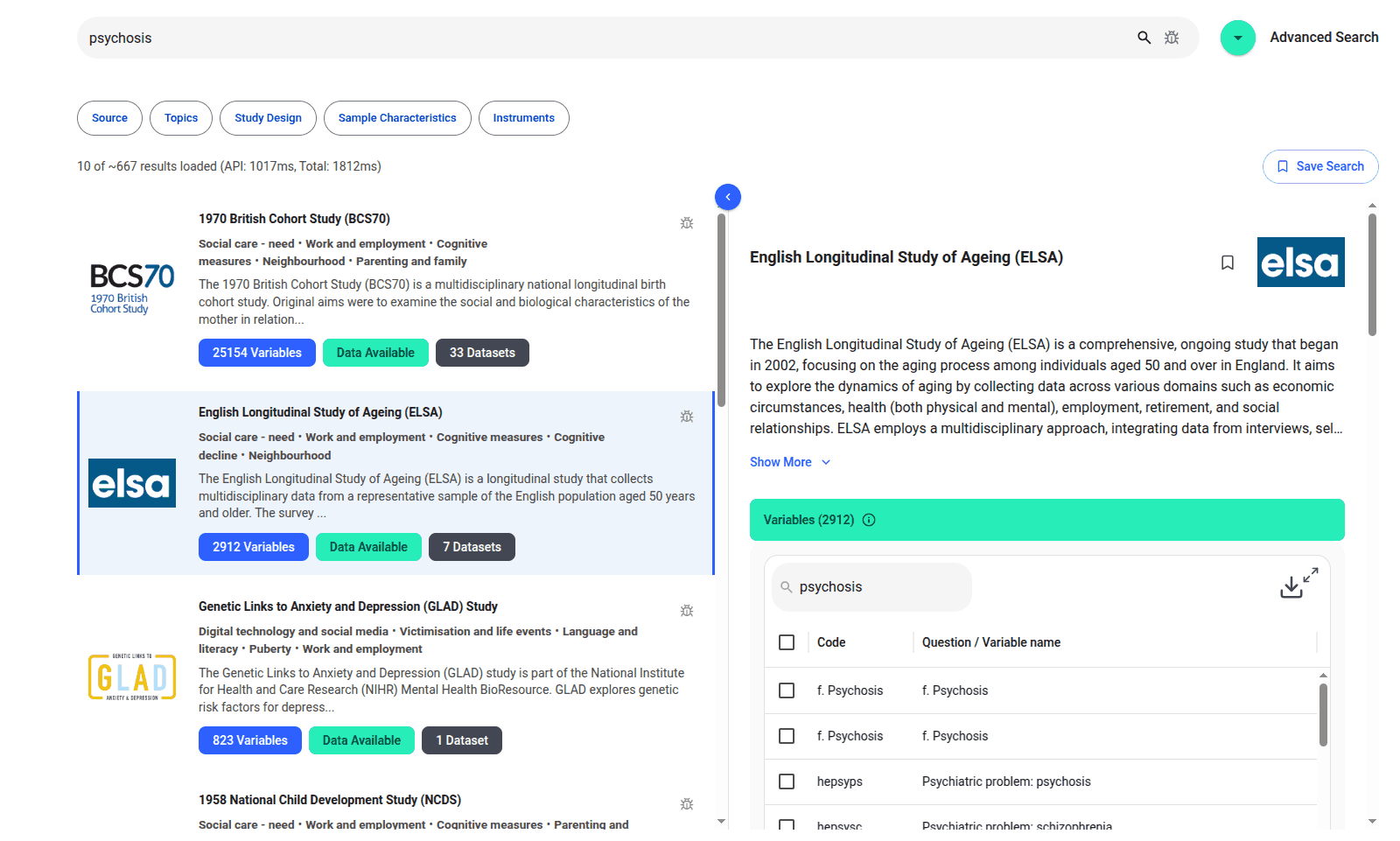
We are excited to introduce the new Harmony Meta platform, which we have developed over the past year. Harmony Meta connects many of the existing study catalogues and registers.

Guest post by Jay Dugad Artificial intelligence has become one of the most talked-about forces shaping modern healthcare. Machines detecting disease, systems predicting patient deterioration, and algorithms recommending personalised treatments all once sounded like science fiction but now sit inside hospitals, research labs, and GP practices across the world.
What we can do for you