We have been developing a tool using Natural Language Processing which is designed to help researchers in the social sciences to harmonise datasets from different contexts. This is part of a wider project called Harmony which is part of an entry we are making to the Wellcome Mental Health Data Prize, together with the Centre for Longitudinal Studies at UCL, Ulster University and Universidade Federal de Santa Maria in Brazil.
The Harmony project is focused on a research question:
How does social connection impact anxiety and depression in young people in different countries?
We have focused on two very different contexts: UK and Brazil. We have explored numerical measures of social connectedness which can be measured in surveys and questionnaires.
The Harmony researchers ran a set of sessions with young people in both countries in order to gather some qualitative data on individual experiences.
In Brazil, our psychologist interviewed 6 people between 13 and 18 who were in treatment for anxiety and depression, and asked them about their concept of social connection and its relation with anxiety and depression.
Fast Data Science - London
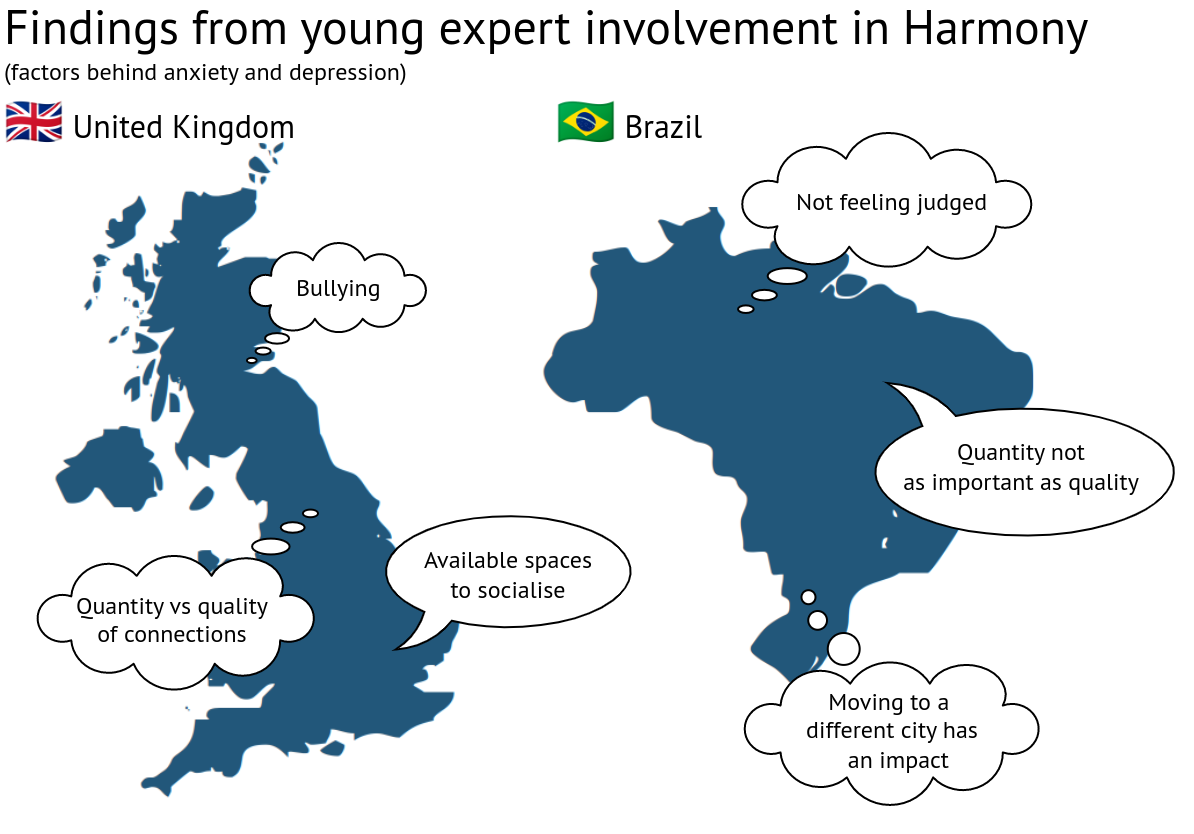
Some differences emerged from these initiatives. For example, British young people mentioned bullying as being a major factor, while Brazilian participants mentioned not feeling judged.
Datasets are available for the UK and Brazil which we were able to work with:
UK Millennium Cohort Study, also known as ‘Child of the New Century’. This is a study by UCL’s Centre for Longitudinal Studies following the lives of around 19,000 young people born in the UK in 2000-02.
Brazilian High Risk Cohort Study for Childhood Psychiatric Disorders (BHRC) is a study that has been following 2,511 Brazilian children since 2010, including psychological, genetic, and neuroimaging data. The aim of the study is to investigate typical and atypical trajectories of psychopathology and cognition over development.
These datasets contain variables and data points which may be presented in a different way. If we want to conduct a meta-analysis (compare the connection between social connection, anxiety and depression in both countries), we would need to first identify what variables are available in both datasets, what variables they have in common, and how we can compare the information in those variables.
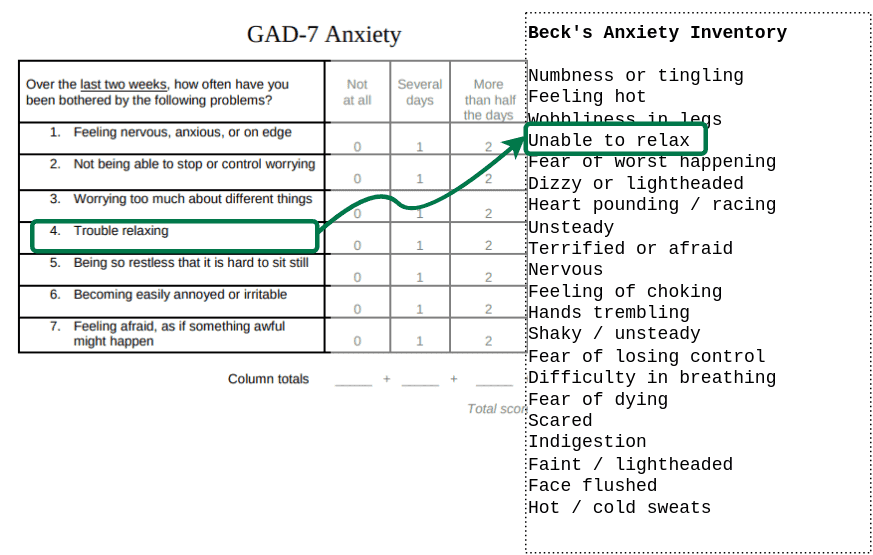
For example, if one study has measured anxiety using the GAD-7 and another has used Beck’s Anxiety Inventory, there would typically be a manual harmonisation process of identifying questionnaire items which are equivalent to one another.
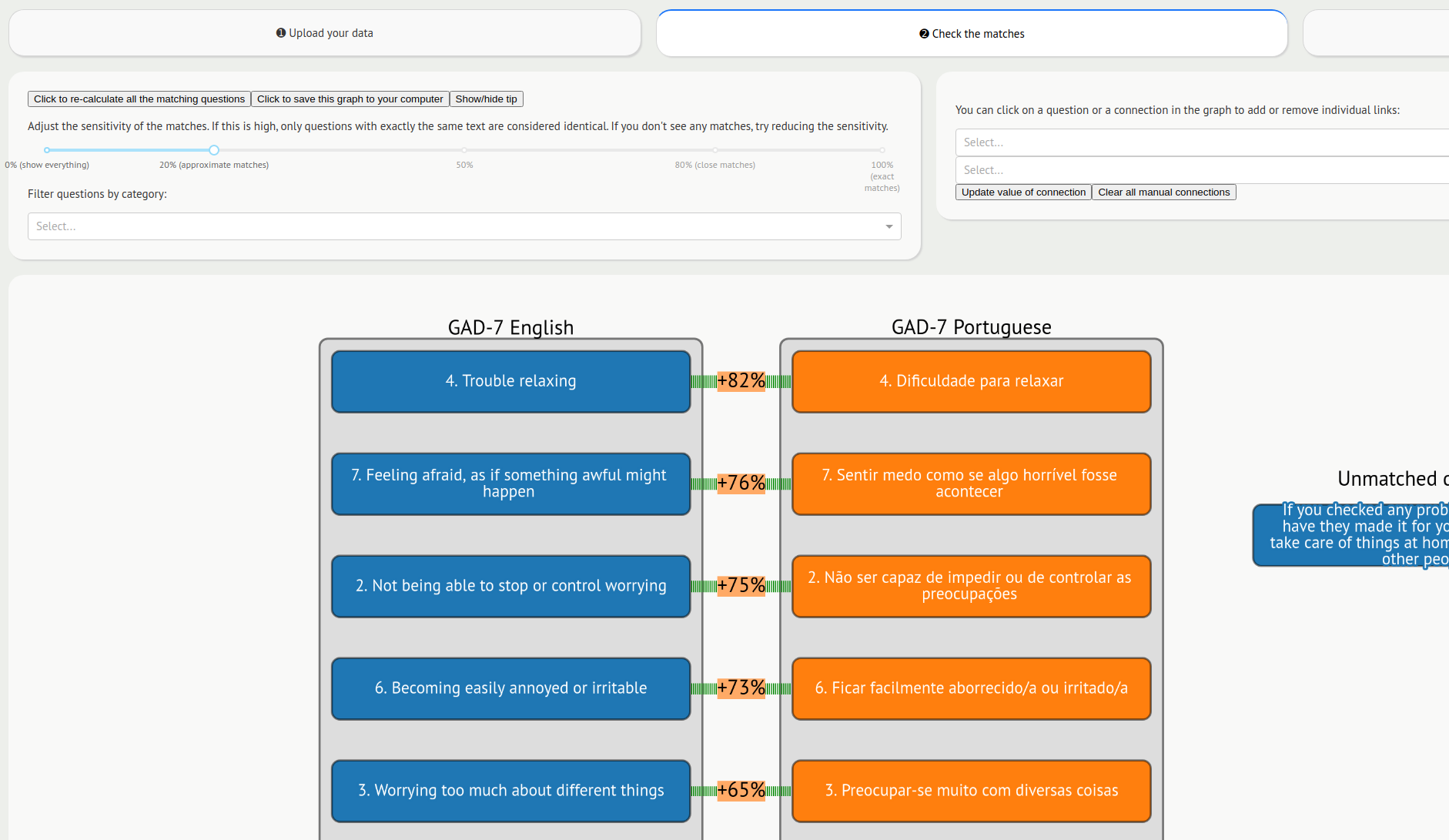
We had the idea of representing each questionnaire item as a vector on the surface of a multi-dimensional sphere. Items which are semantically similar would be close together and have a cosine similarity close to 1, whereas items which are completely different tend to have a similarity close to 0.
We have used the deep learning model GPT-2 to convert texts in different languages into their vector representations. We have wrapped this in a web front-end to make a web-based tool called Harmony. You can try it online at https://harmonydata.ac.uk/app.
We have also developed Harmony in partnership with DATAMIND and the Catalogue of Mental Health Measures, which are widely used resources in psychology research, and taken on board their feedback on how to improve the tool.
You can read about Harmony and how it works on the Harmony blog.
Radford, Alec, et al. “Language models are unsupervised multitask learners.” OpenAI blog 1.8 (2019): 9.
Salum, Giovanni Abrahão. “High Risk Cohort Study for Psychiatric Disorders in Childhood.”
Smith, Kate, and Heather Joshi. “The millennium cohort study.” POPULATION TRENDS-LONDON- (2002): 30-34.
Looking for experts in Natural Language Processing? Post your job openings with us and find your ideal candidate today!
Post a Job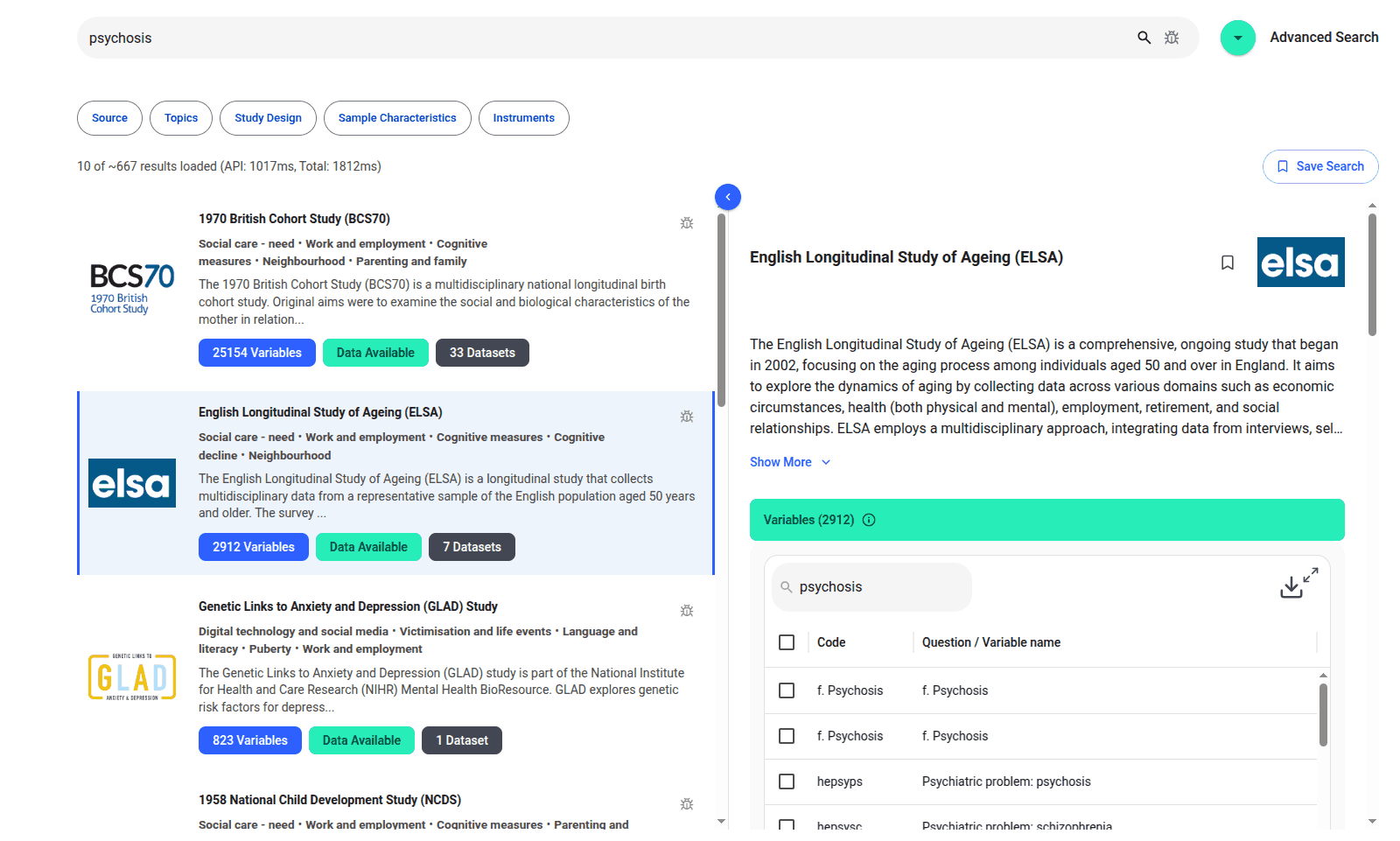
We are excited to introduce the new Harmony Meta platform, which we have developed over the past year. Harmony Meta connects many of the existing study catalogues and registers.

Guest post by Jay Dugad Artificial intelligence has become one of the most talked-about forces shaping modern healthcare. Machines detecting disease, systems predicting patient deterioration, and algorithms recommending personalised treatments all once sounded like science fiction but now sit inside hospitals, research labs, and GP practices across the world.
If you are developing an application that needs to interpret free-text medical notes, you might be interested in getting the best possible performance by using OpenAI, Gemini, Claude, or another large language model. But to do that, you would need to send sensitive data, such as personal healthcare data, into the third party LLM. Is this allowed?
What we can do for you