
Have you ever wondered about the role of AI in data science consulting? Read on and you can learn more about its importance and relevance.
Data science consulting is a relatively new sub-discipline of consulting. Data science consultants are using the latest AI technologies to introduce changes into businesses that can deliver huge returns in terms of profitability. Companies across a wide range of industries are bringing external consultants on board to assist them in making data-driven business decisions and improve outcomes. While it is common for many organisations to have an in-house data science team, scarcity of experts, and the variety of data science specialisms required, means that even large companies are using the services of data science consultants.

At one time, data collection was all about spreadsheets and paper records. Those days are long gone. Now, data can be collected in multiple ways. Machine learning has been in existence since the 1950s but in recent years the technology has moved forwards in leaps and bounds.
Because of the high demand for data science services and the lack of in-house experience in many organisations, a data science consulting model is becoming more and more common.
Today, algorithm implementations have significantly improved so that computers can now not only understand data but learn from it and then make decisions that are based on it. Furthermore, AI allows machines to improve their knowledge when new inputs are added that weren’t part of the original dataset.
AI needs to have sufficient data to learn from. When limited data pools are used to train AI models, the decision-making and prediction accuracy will be low. Therefore, the more data available, the better the AI model’s training and the more accurate the outcome. Faster computer power has paired with the rise of big data, and this has led to many CEOs working on ways of innovating their organisations.
Whenever they are ready to launch new services or products, managers are now looking towards data science to give them insights about demand, market, target demographics, and much more. It comes as no surprise, therefore, that AI and its sub-sets of machine learning and deep learning, are being so readily adopted into the world of enterprise.
Although many large companies now have in-house data science teams, it is often necessary to hire external data science consultants in order to work on the entire data strategy, encompassing data collection, storing, warehousing, model development, analysis, model deployment and maintenance. Public-sector bodies in particular are often unable to hire enough full-time data scientists due to budget constraints and are increasingly resorting to tendering processes to hire data science consultancies on a project basis.
One challenge faced by data science consultants is, how to scope, define, and price projects. Many thought leaders in consultancy, such as Alan Weiss, advocate pricing projects according to the value delivered to the client instead of a day rate, irrespective of the time taken by the consultant.
Consultancies offering services such as software development also commonly use project-based pricing. However, this is still rare in data science consultancy. The main reason is the risk: a data science project has so many unknowns, even halfway through the project, that it is extremely difficult for the consultant to define exactly what will be achievable. For this reason, many data science consultants prefer to charge a day rate.
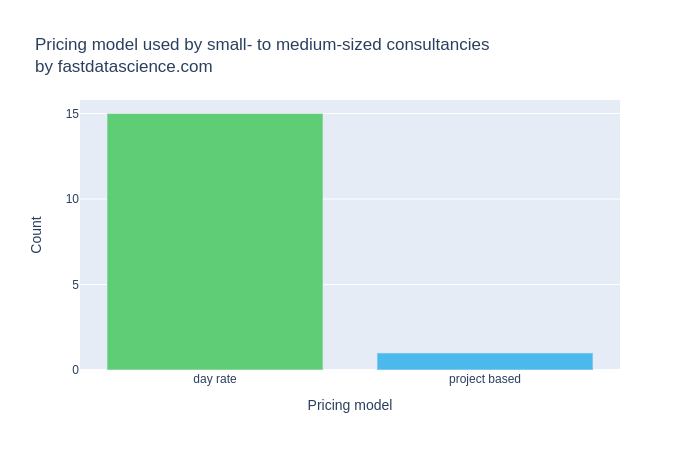
The vast majority of small and medium sized data science consultancies surveyed offered pricing only by day rate rather than on project and milestone basis.
At Fast Data Science, we ran a survey of 16 small to medium-sized data science consultancies across the US and Europe, ranging in size from 1 or 2 people up to 80 people. Nearly all the consultancies typically priced their projects on a day rate, and we were only able to find one which offered project-based or product-based pricing. However, large data science consultancies, such as the Big Four, are able to charge rates high enough to cover the risk, and price their consulting services on a project basis with a money-back guarantee.
We then ran a survey of 10 potential client companies in our network who are hiring data science consultancies, including both customers of ours and non-customers. Of the 10 respondents, 50% actually preferred a project-based payment basis.

50% of customers of data science consultancies in our focus group preferred a project based payment structure
This is interesting, as it exposes a discrepancy between what customers of data science consultancies are looking for, and what the consultancies are offering. In short, both sides want the other to take on the risk. This, for me, is the key differential between data science consultancy and other types of consultancy: risk and the unknown will dominate the conversation and the consultant-client relationship.
Despite this, I would not recommend hiring a large consultancy if you need to bring in an external data science consultant. Large corporations often try to cover all areas, and therefore lack the niche expertise that a boutique data science consultancy can offer. Furthermore, large corporations will charge rates that are more than double those of the smaller consultancies, which is the way that they can swallow the risk.
At Fast Data Science, we specialise in natural language processing. Our domain expertise within this very niche area of data science enables us to deliver a consistent high value to our clients in a very short time. Furthermore, we strategically target industries that naturally contain large amounts of text data, such as healthcare, pharma, insurance, and shipping, enabling us to come onto a client site with both our technical and domain experience and immediately hit the ground running. Although we are not a large corporation, we are willing to offer either project-based or time-based pricing, depending on the client’s preferences.
From the point of view of many of the client companies that we surveyed, it is advantageous to hire a data science consultant with the exact required experience, rather than to go to a large consultancy which claims to be able to offer expertise in all areas of data science.
Companies these days are collecting vast amounts of data, and this data is valuable. With more data, companies can generate business insights that lead to increased revenue. Thanks to data science consultants, it’s possible to uncover patterns within data that would never have been apparent before. Companies are now harnessing these technologies to build recommendation engines, predict user behaviour and more.
Fast Data Science - London
](https://fastdatascience.com/images/111hyn66hcw.jpg)
Data science has been used to combat credit card fraud
The financial sector has begun to heavily use artificial intelligence and data science consultants to detect fraud within financial transactions. TensorFlow and Keras are just two neural network frameworks that data science consultants use for Deep Learning. Using these packages, researchers are able to use ever more sophisticated anomaly detection algorithms to identify fraudulent transactions.
Banks are now able to carefully check the financial transactions, credit scores, and banking history of millions of customers so that they can detect incidences of insurance or loan fraud and prevent them from happening in real time, providing better security and peace of mind to their customers. As a result, a huge amount of money has been saved over the past few years and fraudsters’ jobs have become much harder.
At Fast Data Science, we have undertaken a variety of data science consulting engagements in healthcare. The industry has a large amount of unstructured data that has been locked up by data protection regulations such as GDPR (in Europe) or HIPAA (in the USA), and this means that there’s a large amount of untapped potential for data science to extract value. Because large-scale data science in healthcare is relatively new, and the organisations in question often don’t have in-house data scientists with the right specialisation, it is common to resort to consultants.
For example, the UK’s National Health Service (NHS) advertises regularly for consultancies to assist with data science related problems. The NHS had a problem with large-scale employee attrition. It employs 1.2 million people in the UK, often investing hundreds of thousands of pounds in their training in the case of junior doctors. When a doctor leaves a training pathway, this represents a large monetary loss to the NHS and ultimately to the British taxpayer.
The NHS advertised for data science consultancies on the UK Government’s Digital Marketplace, and Fast Data Science was able to successfully bid for the project together with another data science consultancy. We were able to run an analysis of the NHS’s employee roster to identify common factors behind employees leaving the organisation, and even built a predictive machine learning model which could consume the highly personal data the NHS holds on each employee, and predict the probability of that individual leaving the service. You can read more about the project here.
The analysis and predictive model were taken on board by the NHS management, and implemented into their future policymaking in order to reduce employee turnover.
Pharmaceutical companies have a large volume of text data in the form of manufacturing documents, clinical trial protocols, and scientific literature. Since we specialise in Natural Language Processing at Fast Data Science, we have found this industry to be an ideal focus point for our skillset.
Pharmaceutical companies have brought us on board as data science consultants to:
Another example of the application of AI in the medical domain is IBM Watson Health. This technology uses the power of data science to help physicians rapidly identify vital information in patients’ medical records so relevant evidence can be given and the most suitable treatment options explored. Essentially, it compares a patient’s medical records with information derived from a huge collection of textbooks, texts and journals to give personalised recommendations. As a result, doctors can instantly gain access to a vast wealth of personalised information that is tailored to the individual patient. IBM has been offering data science consulting services to a number of healthcare organisations, such as New York City Social Services.
As well as the healthcare examples cited above, Fast Data Science also undertook some projects for the large UK-based retailer Tesco. This illustrates the versatility of data science skills, and how a data science consultancy can hop across industries with ease.
Tesco has an online grocery ordering system which allows home shopping customers to place orders for delivery. The user interface displays available delivery slots to a customer, they select a slot, and then choose their shopping. The problem faced by Tesco is that a customer may unexpectedly add a large amount of items to their basket after being given a slot, and then the delivery van will not be able to carry all the shopping because it will be overweight.
Fast Data Science came on board as a consultant and was able to implement a predictive model to predict the weight of a customer’s shop in kilograms based on that person’s purchase history, demographic data, and seasonal trends (e.g. the Christmas rush). This allowed Tesco to better anticipate shoppers’ demands and allocate delivery slots to shoppers more efficiently. The supermarket chain was able to reduce the vans used to deliver a fixed amount of shopping by up to 3%. This shows the power of data science consulting in the context of a large company.
These days, the term “fake news” has become highly prevalent. Organisations are frequently being sued for failing to take control of the propagation of untrue news stories on their social platforms. This has led to companies using artificial intelligence paired with data science to detect any fake news that is being circulated on those platforms so that they can take the necessary action to remove the stories before they become widespread.
The other side of the coin is that of course AI models such as GPT-3 can be used to make the task of fake news generation much easier. With minimal (but non-zero) human supervision, AI is now able to write news articles. This month the Guardian published an article titled A robot wrote this entire article. Are you scared yet, human? which brought home the astonishing power that deep learning has achieved when it comes to content creation.

As with all technologies, there are both advantages and disadvantages of AI in data science consulting. Some of the benefits include:
As you might expect, though, there are also some challenges that data science consultancies face. This is especially likely to be the case when AI’s full potential is explored to the limit and not restricted solely to the reproduction of human tasks. Examples of the problems facing the field at the moment include:
As we progress into the third decade of the 21st century, AI and data science are going to become increasingly influential in our lives. Already, many things that were considered to be science fiction are now on the threshold of becoming science fact. Data science is turning some futuristic technologies as self-driving cars into reality. Already, prototype models are being tested and some basic versions are on the roads today.
The world of tomorrow will see fully functioning vehicles that require no driver input to get from A to B. Data science and AI will also pair together to create even more beneficial smart devices, especially those within the healthcare sector. Already there are tiny devices like smartphones that can monitor health parameters such as blood pressure and blood glucose. The most up-to-date smartwatches even have ECG readers. Within the next ten years, it is likely that more cutting-edge devices will be developed that will be primed with a wealth of health data in order to uncover previously unseen wellness patterns in the user to predict future illnesses and medical conditions that will allow users to change their lifestyles at an earlier date.
It is common knowledge that data science will become ubiquitous in our business and personal lives. However, what of the future of consultancy? More and more large businesses are building data science teams. So will there still be a need for data science consultants?
I believe there will always be a need for an experienced data science consultant to provide the niche expertise that is lacking in an in-house team. Often, an external consultant can achieve in a single day what would have taken the in-house team weeks to do. So data science consultants will still be delivering immense value to businesses.
However, I do expect to see a commoditisation and productisation of data science consulting services, as both consultants and clients become more familiar with the capabilities of AI. So data science consultancies will move towards product-based and result-based pricing models, taking on the risk previously shouldered by their clients. Industry standards for data science consulting will become more commonplace and companies will use objective assessments of consulting work. AI will become a staple of the management consultancies, although it will never be their core business.
The data science consulting space will become more crowded, and consultancies will be forced to offer ever more specialised services in order to stand out from the crowd. Certifications will become a must-have for data science consultancies, and this is in their best interests in order to protect the industry from substandard work. As many countries transition towards more informal employment relationships, more and more data scientists will become consultants. Perhaps the big management schools will integrate hands-on data science into their MBA programmes.
If you’re keen to learn more about data science, consultancy, and how the field of artificial intelligence is connected to it, there are many interesting articles that you can read. Some of the most interesting and relevant include The Great Learning Blog’s article “Data Science vs Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence” and the EDUCBA article entitled “Data Science vs Artificial Intelligence.” Both of these will give a greater insight into this topic.
[1] Chatterjee, (Data Science vs Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence: The Difference Explained (2023) )[https://www.mygreatlearning.com/blog/difference-data-science-machine-learning-ai/] (2023)
[2] Kevin Casey, How Big Data And AI Work Together (2019), The Enterprisers Project
[3] Guardian, A robot wrote this entire article. Are you scared yet, human? (2020)
Ready to take the next step in your NLP journey? Connect with top employers seeking talent in natural language processing. Discover your dream job!
Find Your Dream Job
We are excited to introduce the new Harmony Meta platform, which we have developed over the past year. Harmony Meta connects many of the existing study catalogues and registers.

Guest post by Jay Dugad Artificial intelligence has become one of the most talked-about forces shaping modern healthcare. Machines detecting disease, systems predicting patient deterioration, and algorithms recommending personalised treatments all once sounded like science fiction but now sit inside hospitals, research labs, and GP practices across the world.
If you are developing an application that needs to interpret free-text medical notes, you might be interested in getting the best possible performance by using OpenAI, Gemini, Claude, or another large language model. But to do that, you would need to send sensitive data, such as personal healthcare data, into the third party LLM. Is this allowed?
What we can do for you