
‘Data Scientist’ was recently named by LinkedIn as “the most promising career” and according to a report by the US Bureau of Labour Statistics, there will be, on average, a 28% increase across the world in data science jobs by 2026.
You’ll find many more interesting facts claiming how ‘Data Scientist’ is going to be among the most sought after jobs in the 21st century but have you ever wondered how long it takes to become one?
Before we answer this question, it pays to know who a data scientist is and what exactly he/she does.
After all, it can be quite overwhelming for someone considering starting a career in data science to process the plethora of information available online, so we’ve put together this article to bring you up to speed – and of course, answer the above question, while we’re at it!
Data scientists are analytical data specialists who must develop specific technical skills to come up with business solutions using data. They typically manage, analyse, process, model, and interpret data in a way that helps businesses discover trends – and then produce actionable insights to help drive business growth forward.
The everyday data scientist must be proficient in mathematics, computer science and statistics. They must develop extensive industry knowledge (whether that’s in finance or technology, for example) revolving around data and databases, in order to address business challenges. So, a data scientist must wear many ‘technical’ hats, although the bulk of the job revolves around working with data, as one might imagine. At the end of the day, a proficient data scientist is one who is always a curious problem solver and knows how to tap into the power of data to come up with innovative solutions.
As far as roles and responsibilities of a data scientists go, those tend to vary a lot from business to business or from team to team. However, we can certainly draw a few parallels:
Gathering and identifying data sources according to business requirements
Analysing both structured and unstructured (raw) data
Identifying trends and patterns by using a variety of modules and algorithms
Building predictive models and algorithms for the organisation and visualisation of data, and for extracting meaningful insights
Creating, implementing, and maintaining databases while also monitoring data pipelines
Creating solutions and architecture for the entire data processing cycle – from data collection through to data presentation.
“How long will it take me to become a data scientist” is one of the most commonly searched phrases on Google today. Seeing how popular (and important) data science has become over the years, everyone from math geniuses to computer scientists to programmers are exploring the possibility of a lucrative career in this sector – we’ll also discuss the average salaries in the UK in just a bit, so that you have all the knowledge you need to make one of the most important decisions of your life!
Some hopefuls have even gone as far as to key-in search phrases like “Can I become a data scientist in two months”. Well, let’s break it down for you:
First of all, to be very honest, saying that in just a month or two, you can grasp what data science is and how it is applied across different industries to generate business-worthy insights, would be unrealistic and impractical. Sure, you might have seen people becoming data scientists within months and making a really good living too, but those are likely people with extensive knowledge in maths, statistics, machine learning (ML), deep learning (DL), natural language processing (NLP), and what have you.
Now, let’s think about this rationally: to get a rough understanding of what data science is and how you can use it to benefit businesses across different industries, requires a minimum of at least 6-8 months. Furthermore, to find a job in the data science sector, you may need up to a month to build your resume and then look for work in a company which falls in line with your overall career goals. That isn’t etched in stone, however – if you have the right qualifications and experience, you may even be able to land a job within weeks, possibly days.
The subjects we talked about earlier – e.g. maths, machine learning, NLP, etc. – also demand a certain level of expertise and duration in order to ‘qualify’ you as a data scientist. For example:
Maths is a prerequisite for a career in data science. Most schools and colleges cover it and the vast majority of engineering pupils are required to be familiar with it. The foundation of ML or machine learning, for example, a key branch of data science, is statistics, calculus, probability, linear algebra, etc. However, if you have no command over these subjects, then it could take you up to a month to get hands-on knowledge on the various topics within them because you cannot leave one of the key foundations of data science out of the equation – that is, machine learning.
People looking to develop careers in data science must invest a great deal of time in ML. Machine learning is made up of supervised learning and unsupervised learning as well as reinforcement learning.
If you dedicate 1-1.5 months to understand machine learning, for instance, and then another month or so to practice projects and case studies which are based on real-time data, you can significantly improve your chances of becoming a data scientist and that too within a relatively short span of time.
DL is a subset of machine learning and is one of the key components of AI applications as we know them today. In DL, you must acquire insight from large data sets using the Neural Network Algorithm (NNA). It all sounds very hi-tech and interesting, and it is! At least 20 days up to a month are required to properly understand DL.
Fast Data Science - London
Natural language processing is a mix of artificial intelligence (AI), human language, and computer science. It involves functions like topic modelling, text analysis and reprocessing, distance algorithms, information retrieval systems, and much more. A minimum of two weeks are required to gain a thorough understanding of NLP.
Python, R, Java, and C++ are just some of the languages used to implement data science. Python, however, is the most widely used one as it’s easy to understand from the outset, boasts a wide range of libraries and is generally very versatile. If you’re a beginner programmer, you may need up to two months to learn it for data science; if you’re an experienced programmer, you could learn it in a month, on average. You also need to be familiar with libraries like Seaborn, Keras, PyTorch, Pandas, NumPy, XGBoost, etc.
All in all, understanding data science and then applying it in a way which benefits individual business goals takes many months and years of practice. Even data scientists with 10+ years of experience still make mistakes and are in the process of perpetual learning.
Plus, how fast you can become a data scientist also depends on the specific skills you acquire and how good you are at developing them.
If you’ve never worked in data science, that doesn’t mean you can’t become a data scientist fast – that is, as long as develop the right skills.
Since data scientist is a high-level position, you need to first develop a broad knowledge base in your associated field – this could be in statistics, engineering, IT, programming, data analysis, etc. Some data scientists, however, have even started out in finance and baseball scouting.
No matter which field you start out with, your fundamentals need to be strong: Excel, SQL, and Python. Being well-versed in these would allow you to quickly understand how unstructured/raw data is organised. Of course, being familiar with Tableau is a plus, as you may often need to use it to create visualisations.
A data science online boot camp or course can be a great way to build on some data science fundamentals. You’ll learn essentials like collecting and storing data properly, analysing and modelling data using the right methods, and then visualising and presenting that data using a variety of tools.
Once you’re done, you should be able to use R and Python for building models that can analyse behaviour and predict unknowns – exciting stuff!
Data scientists must be good at using different kinds of specialised tools and programmes which specifically cater to data cleaning, analysis, and modelling. For example, apart from being familiar with general-purpose Excel, data scientists must also be familiar with a variety of statistical languages like Hive, R or Python, and query languages like the ever-popular SQL.
Being familiar with RStudio Server is always a plus, as is the open-sourced Jupyter Notebook.
Data science also involves an increasing use of machine learning tools which use AI to allow systems to learn as they go and become more efficient as well as accurate without being explicitly programmed to do so.
Depending on the objectives you’re working with, you can use a broad range of tools, including Apache Mahout, Accord.Net and TensorFlow. The more tools you learn, the better.
After learning some programming language basics and familiarising yourself with popular digital tools that data scientists are currently using, you can put them to use by taking on projects. Always pick projects that allow you to draw on a wide range of skills; for example, using both Excel and SQL to manage as well as query databases; using Python and R to analyse data through statistical methods; building models which analyse behaviour and bring about new insights, and; predicting unknowns through statistical analysis.
The more you practice, the more you should touch on the individual stages in the process – e.g. starting with the initial research of a market sector or company, then identifying and collecting the appropriate data for the given task, and finally, cleaning and testing the data to optimise its usefulness and relevance.
In addition:
Always choose projects which bring into play a broad range of skills and allow you to work with multiple data types
Document the various stages of data analysis – e.g. initial research, defining data, cleaning and testing it, etc. just like we discussed
Create and apply customised algorithms for the purpose of analysing and modelling your data
Package the finalised data into easy-to-understand dashboards or visuals, and then practice presenting it to your friends or family members
It’s always a good idea to get used to practicing with different data types – text, images, structured data, audio, video, etc. Each industry uses unique data types to help make their leadership better and make strategic business decisions – your work will be at the centre of it all!
Once you’ve learned some of the basics, done your preliminary research, gotten the required training, and practiced your skills by working on a range of projects, the next logical step would be develop a nice portfolio that will help you snag your dream data science job.
Your portfolio, in fact, may be your most powerful asset when it comes to the job hunt part.
GitHub is a great place to share your portfolio but you should also share it on a personal website; with all the tools available online, it’s very easy to build your own site. Also, you’d want to showcase the wide range of methods or techniques you used in each one of your projects. Accompany your data with an enticing narrative and context, and, highlight a few pieces related to your dream role.
Remember, your portfolio is a chance to showcase your communication skills as a prospective data scientist – something that’s vital to your success – and demonstrates that you’re capable of a lot more than merely sitting behind a computer and crunching numbers.
Also, just to quickly stress on a previous point, don’t include your entire body of work when applying for a specific role over the GitHub network. Highlight a select few pieces that best relate to the position you are after, as that will showcase the ideal range of skills required for that job.
Businesses are interested in working with data scientists who can offer the critical insights to help them save money or, for example, capture a new market. You must apply the same tried-and-true process to learning as other data scientists do: constantly search for answers to new questions, and keep finding the answers to harder and more complex questions.
Now, if you revisit your projects from, say, two months back and don’t see a whole lot of room for improvement, you’re probably not pushing your boundaries hard enough. You need to be making significant progress each month and your work should be a beaming reflection of that.
Learn to push your boundaries and learn the art of data science faster:
Work with a larger dataset
Practice on projects which require new knowledge and/or skills
Try to make the next project run faster
Teach what you learned during a project to someone else
Since we’re on the subject of answering the ever-important question “How fast can I become a data scientist”, we might as well also answer “How much does a data scientist make”:
According to a recent Glassdoor survey, the average salary of a data scientist in the UK is £45,000. This is based on a sample of 822 salaries although it’s worth bearing in mind that the reported salary range is rather wide – between £30,000 and £70,000 a year. Additional Glassdoor data reveals that large tech companies tend to pay higher salaries compared to other small-midsized firms.
To become a data scientist (fast), you will need a blend of technical and non-technical skills. For example, you should know how to work with data, but at the same time, also to be a good communicator so that you can easily and quickly relay your findings to others.
Here’s how you can become a data scientist as fast as possible:
Nearly all data science jobs require a Bachelor’s degree. Even though some businesses do offer data science positions to applicants without a technical degree, it’s almost always better to graduate in mathematics, computer science, or statistics. You can choose your field according to your interests and know that having a Bachelor’s degree will always give you an edge.
Following graduation, it’s important that you build a specialised skill either through a Master’s degree or by taking a specialisation course in data science. Be very picky when it comes to selecting a course because the course must as a bare minimum have the following:
Lectures or sessions are conducted by industry experts only with proven credentials and at renowned facilities only
The course must fully address your doubts and/or queries, providing you with expert mentorship throughout
The course must include a couple of hands-on projects based on real-world scenarios for you to practice with
The course must award you a certificate upon completion
Once you feel you have a reasonable amount of knowledge and knowhow on data science, you can start looking for entry-level data scientist positions which interest you and appeal to your area of expertise. Always seek out jobs which offer a lot of exposure and opportunities to not only learn but also challenge yourself from time to time.
Specific roles may require different skills although these are needed for virtually any kind of data science role:
Probability and statistics
SQL
Python or R programming skills
Data visualisation
Big data
Communication
Data mining
Building and optimising machine learning (ML) methods
Data analysis
Bear in mind that even though data scientists are expected to know the basics, some roles may require more proficiently with NLP while another one may need you to be an expert at building production-ready predictive algorithms.
The million pound question!
To be fair, the length of time may vary from person to person. We’ve seen people finding a reasonably good position as a data scientist within a year. We’ve also seen people doing it in much less – the key deciding factors are:
The time it takes for you to learn specific processes and techniques around data science
The duration of the job search process which can vary depending on the projects you’ve successfully completed
The qualifications you’ve acquired and your professional background in general
Data scientists in the UK make anywhere between £30,000 and £70,000 a year, according to a report by the National Careers Service.
Yes, there are and you can pursue different kinds of specialisations – e.g. you can work as a data engineer, quantitative analyst, statistician, data architect, machine learning engineer, artificial intelligence engineer, marketing data analyst, and many more.
You’d typically be working in an office environment as the bulk of your work will be done using computers and other IT equipment. Regular travel is not common in data science roles although you may need to travel a little to participate in meetings and/or conferences.
Fast Data Science is always on the lookout for brilliant minds who want to innovate in the field of data science. Get in touch with us now to explore a bright future in one of the most sought after job roles around the globe today.
You may be interested in our blog post on Data science project management
Unleash the potential of your NLP projects with the right talent. Post your job with us and attract candidates who are as passionate about natural language processing.
Hire NLP Experts
Senior lawyers should stop using generative AI to prepare their legal arguments! Or should they? A High Court judge in the UK has told senior lawyers off for their use of ChatGPT, because it invents citations to cases and laws that don’t exist!

Fast Data Science appeared at the Hamlyn Symposium event on “Healing Through Collaboration: Open-Source Software in Surgical, Biomedical and AI Technologies” Thomas Wood of Fast Data Science appeared in a panel at the Hamlyn Symposium workshop titled “Healing Through Collaboration: Open-Source Software in Surgical, Biomedical and AI Technologies”. This was at the Hamlyn Symposium on Medical Robotics on 27th June 2025 at the Royal Geographical Society in London.
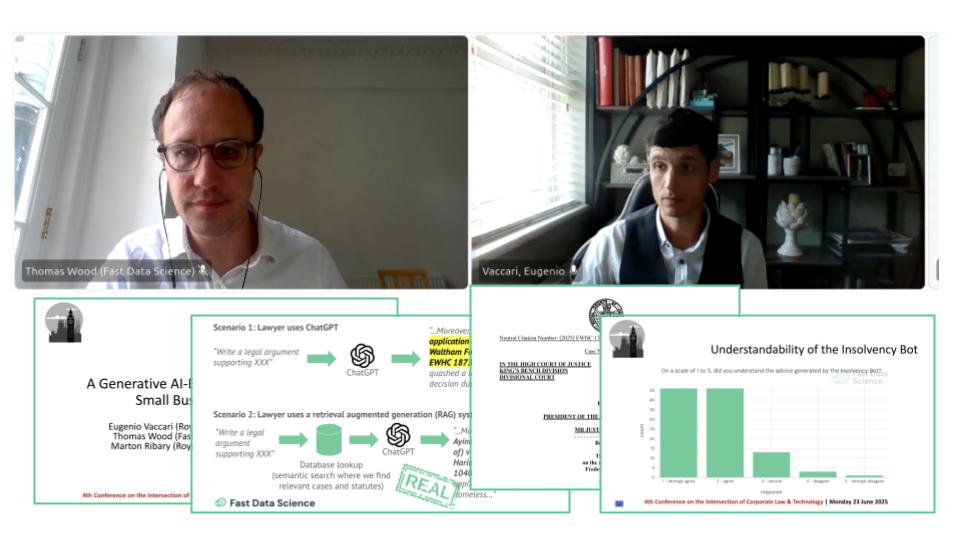
We presented the Insolvency Bot at the 4th Annual Conference on the Intersection of Corporate Law and Technology at Nottingham Trent University Dr Eugenio Vaccari of Royal Holloway University and Thomas Wood of Fast Data Science presented “A Generative AI-Based Legal Advice Tool for Small Businesses in Distress” at the 4th Annual Conference on the Intersection of Corporate Law and Technology at Nottingham Trent University
What we can do for you