
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has permeated almost every sector, bringing significant changes and advancements. The legal industry, traditionally known for its reliance on human expertise and extensive paperwork, is no exception. The advent of AI in law promises to revolutionize various aspects of legal practice, from research and document review to litigation and client interaction. This blog explores the multifaceted impact of AI on the legal field, delving into AI for legal reasoning, litigation, legal AI tools, chatbots, natural language processing, generative AI, the potential of AI replacing lawyers, and the regulatory landscape of legal AI.
Legal reasoning, the process of applying legal rules to specific facts, is at the heart of legal practice. It is a fundamental aspect of legal practice, involving the application of legal rules to specific facts to form arguments and make decisions. AI technologies, particularly those utilizing natural language processing (NLP), can significantly enhance this process by analyzing legal texts and extracting relevant information to support legal arguments.
AI systems in legal reasoning help by:
These capabilities make AI an invaluable tool for lawyers, enhancing their ability to deliver precise, informed, and high-quality legal advice.
Natural language processing
Litigation involves numerous time-consuming tasks such as document review, evidence analysis, and case preparation. AI streamlines these processes by automating the review of documents, identifying relevant information, and predicting case outcomes based on historical data. The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in litigation can significantly streamline these processes, enhancing both efficiency and accuracy. Over the past five years, the adoption of AI tools has significantly transformed various aspects of legal practice, improving efficiency and reducing costs.
Key applications of AI in litigation include:
AI’s role in litigation is not just about reducing labor and time; it also brings precision and a data-driven approach that can lead to more informed decision-making and potentially better outcomes for clients.
A variety of AI tools have emerged to support legal professionals in their daily tasks. These tools leverage machine learning algorithms to automate routine processes, enhance research capabilities, and improve decision-making. Popular legal AI tools are:
Natural language processing
AI-powered chatbots are becoming an integral part of legal services, offering immediate assistance and basic legal advice to clients. These chatbots use NLP to understand and respond to queries, providing information on legal procedures, rights, and obligations. By automating initial consultations, legal chatbots free up valuable time for lawyers and make legal assistance more accessible to the public. Examples include DoNotPay, a chatbot that helps users contest parking tickets, and LawDroid, which assists in legal form completion and information gathering.
Legal AI chatbots are a prime example of how AI can enhance the delivery of legal services, making them more efficient and accessible while maintaining a high standard of initial legal guidance. As technology advances, these tools are expected to become even more sophisticated, further integrating into the practices of law firms and legal departments globally.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a pivotal technology in legal AI, enabling machines to understand and interact with human language. This capability is especially valuable in the legal industry, where the interpretation and analysis of textual data are foundational tasks.
Case Law Research:
Contract Review:
NLP is transforming how legal work is done, from improving the speed and precision of legal research to enhancing the thoroughness of document reviews. As NLP technologies continue to evolve, their integration into legal practices is expected to deepen, further revolutionizing the industry.
Generative AI, which involves creating new content based on existing data, holds significant potential in the legal field. Its ability to automate and enhance several key processes can drastically improve efficiency and accuracy in legal practices.
Drafting Legal Documents:
Summarizing Case Law:
Automated Briefs:
Generative AI is set to transform the legal industry by automating tasks that traditionally require extensive manual labor, thereby allowing lawyers to optimize their time and resources. As this technology evolves, its integration into legal practices is expected to deepen, bringing about further efficiencies and innovations.
The question of whether Artificial Intelligence (AI) can replace lawyers is complex and nuanced. While AI has demonstrated its capacity to handle many tasks traditionally performed by lawyers, such as document review, legal research, and contract analysis, there are significant limitations to its capabilities.
AI systems do not possess the human-like ability to understand context in the way lawyers do when interpreting laws and legal precedents. They operate based on data and patterns rather than a comprehensive understanding of legal principles. AI lacks the capability to make ethical decisions. The ethical judgment required in legal practice involves considerations that extend beyond the data, something current AI technology cannot replicate. AI does not have the ability to engage in creative thinking or empathize with human emotions, both of which are crucial in many aspects of legal work, particularly in negotiations, advocacy, and client interactions.
Rather than replacing lawyers, AI is more effective as a tool that augments their capabilities. It can automate routine tasks, thereby allowing lawyers to focus on more complex, strategic legal work that requires human insight. AI can significantly enhance the efficiency of legal processes. For example, by automating document analysis and legal research, lawyers can access information and insights more quickly and accurately. With AI handling repetitive and data-intensive tasks, lawyers can dedicate more time to activities that add greater value, such as formulating legal strategies, engaging in client consultations, and making court appearances.
AI is transforming the legal industry by enhancing the capabilities of legal professionals and improving the efficiency of legal services. However, it is unlikely to replace lawyers entirely due to its limitations in understanding context, making ethical judgments, and replicating human empathy and creativity. Instead, AI will continue to serve as a powerful tool that supports lawyers in their professional roles.
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into the legal field has introduced various applications that enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of legal services. Below are key areas where AI is making significant impacts.
The rise of legal AI also brings regulatory challenges that must be addressed to ensure ethical and responsible use. Key considerations include:
Legal research and document review are fundamental tasks in legal practice, often involving the analysis of vast amounts of information. AI enhances these tasks by:
E-discovery, the process of identifying, collecting, and producing electronically stored information (ESI) in response to a legal request, is a labor-intensive task. AI simplifies e-discovery by:
Contracts are the backbone of legal agreements, and thorough review is essential to ensure compliance and mitigate risks. AI aids in contract review and due diligence by:
Predictive analytics involves using historical data to forecast future outcomes. In the legal field, AI-driven predictive analytics can:
The future of legal AI is promising, with continuous advancements in technology likely to bring even more sophisticated tools and applications. Here are some potential future developments in the field:
The continued integration of AI into the legal field suggests a transformative shift towards more efficient, accessible, and cost-effective legal services. As technology progresses, the role of AI in legal practices is set to expand, potentially reshaping the profession in fundamental ways.
The adoption of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the legal sector raises significant ethical and societal questions that must be addressed to ensure responsible integration. Below are some of the key considerations:
The Law Society of England and Wales: This body has issued protocols and ethics opinions concerning the use of AI in legal practice, focusing on maintaining client confidentiality, data protection, and the integrity of legal advice.
UNESCO Recommendations on the Ethics of AI: While broader in scope, these recommendations address ethical considerations that apply to the use of AI in all fields, including legal practices, emphasizing respect for human rights and fundamental freedoms.
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): This European regulation impacts how AI can be used with personal data, particularly concerning data protection and privacy in legal scenarios.
Ethical Guidelines for AI in Legal Systems (Georgetown University): Various countries and legal bodies have proposed ethical guidelines to ensure AI is used responsibly in legal contexts. These guidelines typically address issues like transparency, accountability, and fairness in AI applications.
ABA Model Rules of Professional Conduct: While not specifically tailored to AI, these rules by the American Bar Association guide lawyers in the U.S. on how to responsibly incorporate technology into their practice, which indirectly applies to AI tools.
ALTA (Australian Legal Technology Association) Principles: ALTA provides principles specifically designed to guide the development and application of legal technologies, including AI, in ways that uphold legal and ethical standards.
The integration of AI into the legal sector offers immense potential but also presents complex ethical challenges. Addressing these effectively will require ongoing dialogue among legal professionals, technologists, and policymakers to ensure that the benefits of legal AI are realized without compromising ethical standards or societal values.
Legal AI is revolutionizing the legal industry by enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and accessibility, transforming various aspects of legal services including legal reasoning, litigation, research, and contract review. While AI cannot replace the nuanced judgment and strategic thinking of human lawyers, it serves as a powerful tool that augments their capabilities, allowing them to focus more on higher-value activities. We are still working out how to regulate the use of AI, in particular generative AI, in the legal profession, as recent cases involving documents submitted to Court containing fake citations have shown.
As AI technology continues to evolve, addressing the ethical and regulatory challenges is crucial to ensure that its benefits are fully realized while maintaining the integrity of the legal profession. The future holds immense potential for even more sophisticated AI tools that will further transform legal services, making it essential for ongoing collaboration among legal professionals, technologists, and policymakers to develop frameworks that ensure responsible and fair use of AI in law.
Unleash the potential of your NLP projects with the right talent. Post your job with us and attract candidates who are as passionate about natural language processing.
Hire NLP Experts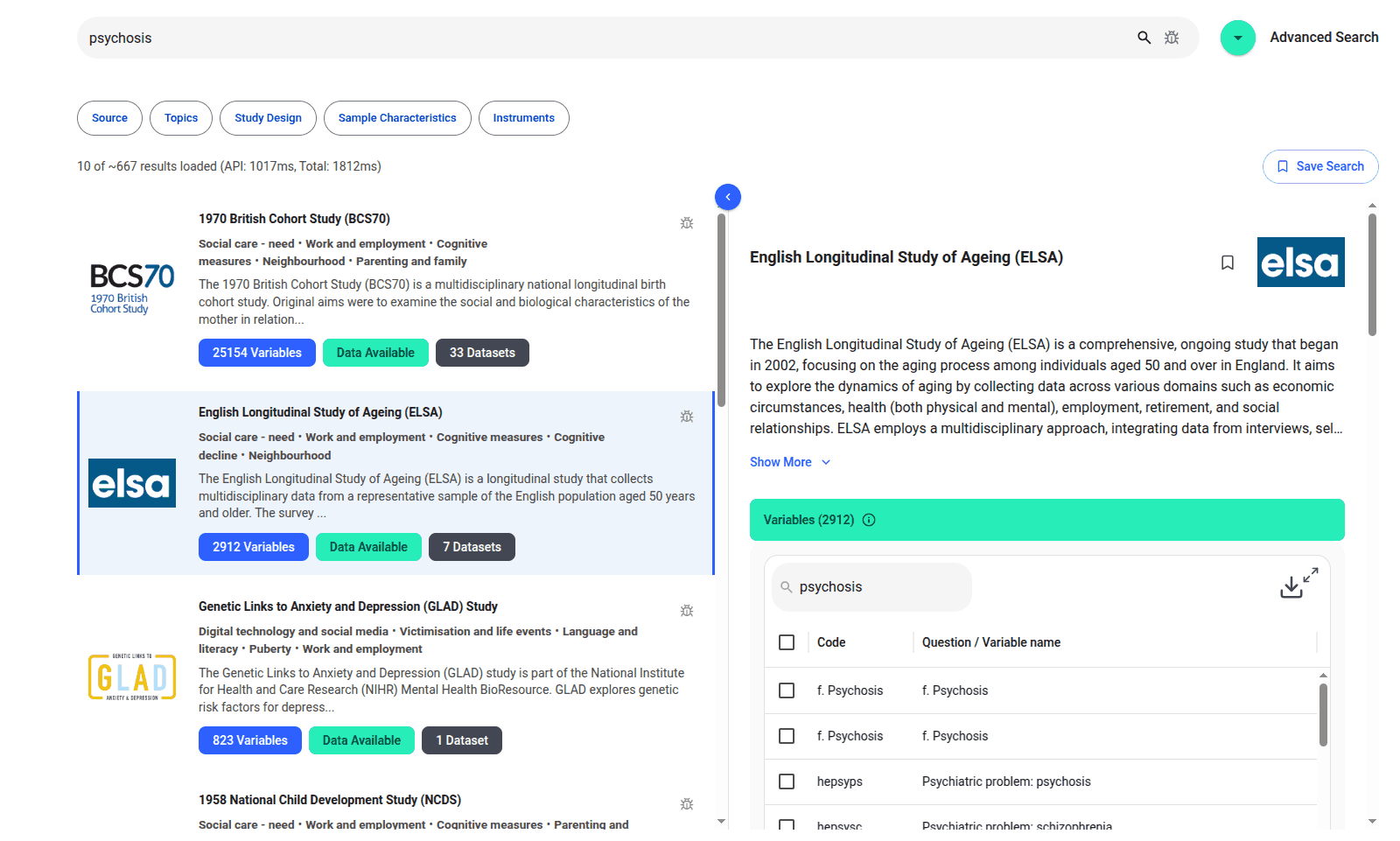
We are excited to introduce the new Harmony Meta platform, which we have developed over the past year. Harmony Meta connects many of the existing study catalogues and registers.

Guest post by Jay Dugad Artificial intelligence has become one of the most talked-about forces shaping modern healthcare. Machines detecting disease, systems predicting patient deterioration, and algorithms recommending personalised treatments all once sounded like science fiction but now sit inside hospitals, research labs, and GP practices across the world.
If you are developing an application that needs to interpret free-text medical notes, you might be interested in getting the best possible performance by using OpenAI, Gemini, Claude, or another large language model. But to do that, you would need to send sensitive data, such as personal healthcare data, into the third party LLM. Is this allowed?
What we can do for you